- February 15, 2023
- Posted by: Manish Kandel
- Category: Blog/Article
The Lean Startup is a concept introduced by Eric Ries in his book “The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses.” It is a methodology for developing and launching successful startups that emphasizes a rapid, iterative, and customer-focused approach.
In summary, lean startup is a methodology designed to validate a business hypothesis through short and rapid release cycles of product features, business models, and strategies; and the concept is designed to reduce market risk by validating learning through the release of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) i.e., designing a low barrier to entry first version of a product, so that it can start driving value sooner, and then iterating on it consistently to add more improvements and functionality.
“Startup success can be engineered by following the process, which means it can be learned, which means it can be taught.” -Eric Ries
Eliminate Uncertainty
The lack of a tailored management process has led many a start-up or, as Ries terms them, “a human institution designed to create a new product or service under conditions of extreme uncertainty”, to abandon all processes. They take a “just do it” approach that avoids all forms of management. But this is not the only option. Using the Lean Startup approach, companies can create order not chaos by providing tools to test a vision continuously. Lean isn’t simply about spending less money. Lean isn’t just about failing fast, failing cheap. It is about putting a process, a methodology around the development of a product.
Work Smarter Not Harder
The Lean Startup methodology has as a premise that every startup is a grand experiment that attempts to answer a question. The question is not “Can this product be built?” Instead, the questions are “Should this product be built?” and “Can we build a sustainable business around this set of products and services?” This experiment is more than just theoretical inquiry; it is a first product. If it is successful, it allows a manager to get started with his or her campaign: enlisting early adopters, adding employees to each further experiment or iteration, and eventually starting to build a product. By the time that product is ready to be distributed widely, it will already have established customers. It will have solved real problems and offer detailed specifications for what needs to be built.
Develop an MVP
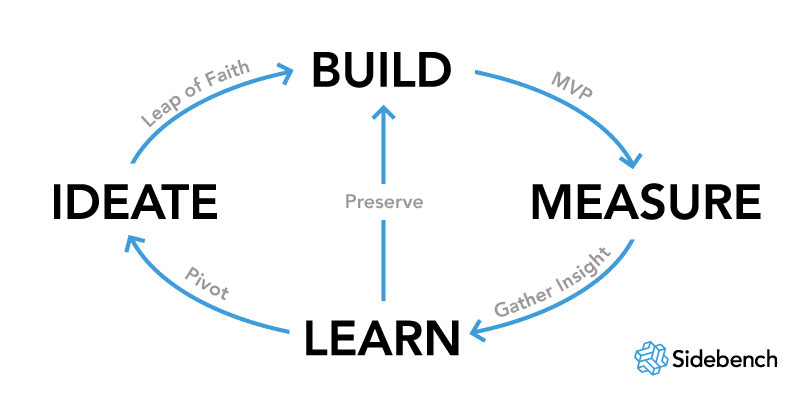
A core component of Lean Startup methodology is the build-measure-learn feedback loop. The first step is figuring out the problem that needs to be solved and then developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to begin the process of learning as quickly as possible. Once the MVP is established, a startup can work on tuning the engine. This will involve measurement and learning and must include actionable metrics that can demonstrate cause and effect questions.
The startup will also utilize an investigative development method called the “Five Whys”-asking simple questions to study and solve problems along the way. When this process of measuring and learning is done correctly, it will be clear that a company is either moving the drivers of the business model or not. If not, it is a sign that it is time to pivot or make a structural course correction to test a new fundamental hypothesis about the product, strategy and engine of growth.
Validated Learning
Progress in manufacturing is measured by the production of high quality goods. The unit of progress for Lean Startups is validated learning-a rigorous method for demonstrating progress when one is embedded in the soil of extreme uncertainty. Once entrepreneurs embrace validated learning, the development process can shrink substantially. When you focus on figuring the right thing to build-the thing customers want and will pay for-you need not spend months waiting for a product beta launch to change the company’s direction. Instead, entrepreneurs can adapt their plans incrementally, inch by inch, minute by minute.
Lean Startup Methodology Summary
Just because other businesses may have had success with following a traditional startup growth strategy, it doesn’t mean you have to. The lean startup methodology is a way for you to use a feedback loop to test your business idea. The build-measure-learn loop is a way for you to see if there’s customer interest in your idea. If there’s not, you can use the data from your test to help you pivot and change your business plan.
The goal of the lean startup approach is to minimize waste, reduce risks, and increase the chances of success by focusing on what customers really want and need. This is accomplished by using customer feedback to validate assumptions and make data-driven decisions.
This concept is widely used in the startup ecosystem to validate business ideas, product development, and scaling strategies. It can also be applied to large enterprises and government organizations to drive innovation and improve processes.
By: Swornin Lama | BIC Alumnus
